基本概念 Java反射机制 反射是Java 编程语言中的一个特性。它允许正在执行的Java 程序检查或“内省”自身,并操纵程序的内部属性。 例如,Java类可以获取其所有成员的名称并显示它们。因此,反射提供了以下一些功能:
获取某个类定义的方法信息,包括方法名,参数,返回值等信息。 获取某个类的构造函数。 获取某个类的属性。 通过方法名调用类的相应的方法。 修改对象的属性值。 创建某个类对应的对象。 更多反射的详情可以参考文章
Java内省机制 使用内省相对于直接使用反射更加安全可靠,Java的反射机制比较特殊,它不同于一般的编程方式,稍不小心就容易破坏类的封装性。练的不好,就容易走火入魔。没关系,很多时候我们还可以使用Java的内省机制。
Java的内省机制是什么? 在计算机科学中,内省是指计算机程序在运行时(Run time)检查对象(Object)类型的一种能力,通常也可以称作运行时类型检查。
内省(Introspection )在心理学中,它是心理学基本研究方法之一。内省法又称自我观察法。它是发生在内部的,我们自己能够意识到的主观现象。也可以说是对于自己的主观经验及其变化的观察。正因为它的主观性,内省法自古以来就成为心理学界长期的争论。争论于它是否客观,是否可靠。另外内省也可看作自我反省,也是儒家强调的自我思考。从这个角度说它可以应用于计算机领域,例如Java内省机制和cocoa内省机制。
Java语言内省(Introspector)是Java语言对Bean类属性、事件的一种缺省处理方法。例如类A中有属性name,那我们可以通过getName,setName来得到其值或者设置新的值。通过getName/setName来访问name属性,这就是默认的规则。Java中提供了一套API用来访问某个属性的getter/setter方法,通过这些API可以使你不需要了解这个规则(但你最好还是要搞清楚),这些API存放于包java.beans中。
以上就是百科的解释。Java的内省最终是用Java的反射实现的。那为什么不直接用反射,要使用内省呢?
在Java中,内省的实现为:
内省(Introspector)是Java语言对Bean类属性、事件的一种缺省处理方法。 例如类A中有属性name,那我们可以通过getName,setName来得到其值或者设置新的值。 通过getName/setName来访问name属性,这就是默认的规则。 Java中提供了一套API用来访问某个属性的getter/setter方法,通过这些API可以使你不需要了解这个规则, 这些API存放于包java.beans中。 一般的做法是通过类Introspector来获取某个对象的BeanInfo信息, 然后通过BeanInfo来获取属性的描述器(PropertyDescriptor), 通过这个属性描述器就可以获取某个属性对应的getter/setter方法, 然后我们就可以通过反射机制来调用这些方法。 内省(Introspector) 内省(Introspector): 是指对 JavaBean 类属性、事件处理的一套方法。内省就是基于反射实现的,是对反射的一种封装。
理解:
(1)对于一个普通的javabean,反射可以用Class<?>(字节码文件对象类)对这个javabean进行描述,描述这个普通的javabean的类型、属性信息、构造器信息、方法信息等,进而可以通过这些信息动态创建对象来使用;而内省就是对于一个普通的javabean,将这个javabean所有的属性信息、构造器信息、方法信息等封装(或构造)成一个新的beaninfo对象,然后用Introspector类来对这个beaninfo进行操作,进而来获得BeanDescriptor(bean描述器)、PropertyDescriptor(属性描述器)、MethodDescriptor(方法描述器)、 EventSetDescriptor(事件描述器)等
(2)内省的具体体现
例如:我们对idea中代码字体的大小进行设置,我们在设置框中字体大小栏输入12或16等时,可以看到下方的示例字体大小也随之发生改变,这里就用到了内省机制中的事件监听,若有变化则自我感知从而发生改变;
还例如:在反射中我们说对于一个User.java类,当new一个对象后,User user = new User();我们可以通过user. 的形式来知道这个对象中封装了哪些方法,像我们可以这样 Integer id = user.getId();来获取id,但是假如我们现在将User.java中的属性id的类型由Integer id 改为 String id,这样方法会立即报错,我们在其他地方使用的user.getId也会报错,这就是用内省机制来完成的,它有对这种类型检查的机制或事件监听的机制,若有变化自我感知从而发生改变。
JavaBean是什么 JavaBean是一种特殊(其实说普通也可以,也不是十分特殊)的类,主要用于传递数据信息,这种类中的方法主要用于访问私有的字段,且方法名符合某种命名规则(字段都是私有,每个字段具备Setter和Getter方法,方法和字段命名满足首字母小写驼峰命名规则)。如果在两个模块之间传递信息,可以将信息封装进JavaBean中,这种对象称为值对象(Value Object)或者VO。这些信息储存在类的私有变量中,通过Setter、Getter方法获得。JavaBean的信息在Introspector里对应的概念是BeanInfo,它包含了JavaBean所有的Descriptor(描述符),主要有PropertyDescriptor,MethodDescriptor(MethodDescriptor里面包含ParameterDescriptor)、BeanDescriptor和EventSetDescriptor。
属性Field和属性描述PropertiesDescriptor的区别 如果是严格的JavaBean(Field名称不重复,并且Field具备Setter和Getter方法),它的PropertyDescriptor会通过解析Setter和Getter方法,合并解析结果,最终得到对应的PropertyDescriptor实例。所以PropertyDescriptor包含了属性名称和属性的Setter和Getter方法(如果存在的话)。
内省Introspector和反射Reflection的区别 Reflection:反射就是运行时获取一个类的所有信息,可以获取到类的所有定义的信息(包括成员变量,成员方法,构造器等)可以操纵类的字段、方法、构造器等部分。可以想象为镜面反射或者照镜子,这样的操作是带有客观色彩的,也就是反射获取到的类信息是必定正确的。Introspector:内省基于反射实现,主要用于操作JavaBean,基于JavaBean的规范进行Bean信息描述符的解析,依据于类的Setter和Getter方法,可以获取到类的描述符。可以想象为“自我反省”,这样的操作带有主观的色彩,不一定是正确的(如果一个类中的属性没有Setter和Getter方法,无法使用内省)。内省常用API 内省涉及到的主要的类与接口如下:
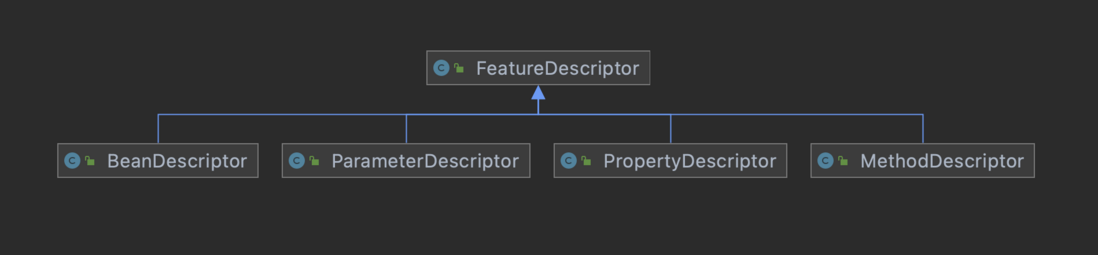
Introspector 类: 提供标准的方式来获取Java Bean支持的属性,事件和方法等信息,它提供了的 getBeanInfo 系类方法,可以拿到一个 JavaBean 的所有信息。BeanInfo 接口: 定义了获取上述 Java Bean 信息的接口,通过 BeanInfo 的 getPropertyDescriptors 方法和 getMethodDescriptors 方法可以拿到 javaBean 的字段信息列表和 getter 和 setter 方法信息列表。FeatureDescriptor: 是 PropertyDescriptor、EventSetDescriptor 和 MethodDescriptor 等的公共基类,它支持一些可以设置和获取任意的内省描述符的公共信息。PropertyDescriptors 可以根据字段直接获得该字段的 getter 和 setter 方法。MethodDescriptors 可以获得方法的元信息,比如方法名,参数个数,参数字段类型等。
FeatureDescriptor 的主要属性有:
private boolean expert;private boolean hidden;private boolean preferred;private String shortDescription;private String name;private String displayName;private Hashtable<String, Object> table;
Introspector Introspector类似于BeanInfo的静态工厂类,主要是提供静态方法通过Class实例获取到BeanInfo,得到BeanInfo之后,就能够获取到其他描述符。主要方法:
public static BeanInfo getBeanInfo(Class beanClass):通过Class实例获取到BeanInfo实例。BeanInfo BeanInfo是一个接口,具体实现是GenericBeanInfo,通过这个接口可以获取一个类的各种类型的描述符。主要方法:
BeanDescriptor getBeanDescriptor():获取JavaBean描述符。EventSetDescriptor[] getEventSetDescriptors():获取JavaBean的所有的EventSetDescriptor。PropertyDescriptor[] getPropertyDescriptors():获取JavaBean的所有的PropertyDescriptor。MethodDescriptor[] getMethodDescriptors():获取JavaBean的所有的MethodDescriptor。这里要注意一点,通过BeanInfo#getPropertyDescriptors()获取到的PropertyDescriptor数组中,除了Bean属性的之外,还会带有一个属性名为class的PropertyDescriptor实例,它的来源是Class的getClass方法,如果不需要这个属性那么最好判断后过滤。
PropertyDescriptor PropertyDescriptor类表示JavaBean类通过存储器(Setter和Getter)导出一个属性,它应该是内省体系中最常见的类。主要方法:
synchronized Class getPropertyType():获得属性的Class对象。synchronized Method getReadMethod():获得用于读取属性值的方法;synchronized Method getWriteMethod():获得用于写入属性值的方法。int hashCode():获取对象的哈希值。synchronized void setReadMethod(Method readMethod):设置用于读取属性(Getter)值的方法。synchronized void setWriteMethod(Method writeMethod):设置用于写入属性值(Setter)的方法。举个例子:
public class Main public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Person.class); PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) { if (!"class" .equals(propertyDescriptor.getName())) { System.out.println(propertyDescriptor.getName()); System.out.println(propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod().getName()); System.out.println(propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod().getName()); System.out.println("=======================" ); } } } public static class Person private Long id; private String name; private Integer age; public Long getId () return id; } public void setId (Long id) this .id = id; } public String getName () return name; } public void setName (String name) this .name = name; } public Integer getAge () return age; } public void setAge (Integer age) this .age = age; } } }
输出结果:
age setAge getAge ======================= id setId getId ======================= name setName getName =======================
不正当使用Introspector会导致内存溢出 如果框架或者程序用到了JavaBeans Introspector,那么就相当于启用了一个系统级别的缓存,这个缓存会存放一些曾加载并分析过的Javabean的引用,当web服务器关闭的时候,由于这个缓存中存放着这些Javabean的引用,所以垃圾回收器不能对Web容器中的JavaBean对象进行回收,导致内存越来越大。还有一点值得注意,清除Introspector缓存的唯一方式是刷新整个缓存缓冲区,这是因为JDK没法判断哪些是属于当前的应用的引用,所以刷新整个Introspector缓存缓冲区会导致把服务器的所有应用的Introspector缓存都删掉。Spring中提供的org.springframework.web.util.IntrospectorCleanupListener就是为了解决这个问题,它会在Web服务器停止的时候,清理一下这个Introspector缓存,使那些Javabean能被垃圾回收器正确回收。
也就是说JDK的Introspector缓存管理是有一定缺陷的。但是如果使用在Spring体系则不会出现这种问题,因为Spring把Introspector缓存的管理移交到Spring自身而不是JDK(或者在Web容器销毁后完全不管),在加载并分析完所有类之后,会针对类加载器对Introspector缓存进行清理,避免内存泄漏的问题,详情可以看CachedIntrospectionResults和SpringBoot刷新上下文的方法AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()中finally代码块中存在清理缓存的方法AbstractApplicationContext#resetCommonCaches();。但是有很多程序和框架在使用了JavaBeans Introspector之后,都没有进行清理工作,比如Quartz、Struts等,这类操作会成为内存泄漏的隐患。
内省的使用方式 使用步骤:
获取BeanInfo 获取Descriptor 具体的示例如下:
public class IntrospectorExample public static void main (String[] args) try { BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Person.class); BeanDescriptor beanDescriptor = beanInfo.getBeanDescriptor(); System.out.println("BeanName:" + beanDescriptor.getName()); PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) { Object defaultValue = new Object(); if (propertyDescriptor.getPropertyType().equals(Integer.TYPE)) { defaultValue = 0 ; } else if (propertyDescriptor.getPropertyType().equals(String.class)) { defaultValue = "Empty String" ; } propertyDescriptor.setValue("default" , defaultValue); System.out.println("name:" + propertyDescriptor.getName() + ", displayName:" + propertyDescriptor.getDisplayName() + ", type:" + propertyDescriptor.getPropertyType() + ", isExpert: " + propertyDescriptor.isExpert() + ", isConstrained: " + propertyDescriptor.isConstrained() + ", isHidden: " + propertyDescriptor.isHidden() + ", isPreferred: " + propertyDescriptor.isPreferred() + ", isBound: " + propertyDescriptor.isBound() + ", readMethod:" + propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod() + ",writeMethod:" + propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod() + ", value:" + propertyDescriptor.getValue("default" )); } MethodDescriptor[] methodDescriptors = beanInfo.getMethodDescriptors(); for (MethodDescriptor methodDescriptor : methodDescriptors) { System.out.print("methodName:" + methodDescriptor.getName() + ", methodDisplayName:" + methodDescriptor.getDisplayName() + ", method:" + methodDescriptor.getMethod()); ParameterDescriptor[] parameterDescriptors = methodDescriptor.getParameterDescriptors(); if (null == parameterDescriptors) { System.out.println(); continue ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < parameterDescriptors.length; i++) { System.out.print(", #" + i + "paramName" + parameterDescriptors[i].getName() + ", paramClass" + parameterDescriptors[i].getClass()); } System.out.println(); } } catch (IntrospectionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Introspector java.beans.Introspector,即内省。它提供了一套标准的访问Java Bean的属性,事件以及方法的处理方法。 对于Java Bean的这3种信息,Introspector会分析Java Bean以及它的父类的显示和隐式的信息,然后构建一个全面描述此Java Bean的BeanInfo对象。
在Java中,JavaBean是一种特殊的类,主要用于传递数据信息,这种类中的方法主要用于访问私有的属性,且方法名符合某种命名规则。例如DTO,VO等,我们在业务或者模块之间传递信息,可以将信息封装到JavaBean中。
既然封装到JavaBean中,那就会有设置(setter)和读取(getter)JavaBean中私有属性等操作。Introspector可以帮我们做到这件事,不过要注意,JavaBean中的getter和setter等方法要遵循某种规范。(驼峰规则)
public class Person private String id; private String name; private int age; public Person (String id, String name, int age) this .id = id; this .name = name; this .age = age; } public String getId () return id; } public void setId (String id) this .id = id; } public String getName () return name; } public void setName (String name) this .name = name; } public int getAge () return age; } public void setAge (int age) this .age = age; } }
public class Demo public static void main (String[] args) throws IntrospectionException BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Person.class, Object.class); BeanInfo includeParentBeanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Person.class); } }
BeanInfo java.beans.BeanInfo是一个接口,它有几个默认的实现类,我们一般默认生成的BeanInfo对象其实是GenericBeanInfo类的实例。简而言之,BeanInfo对象能提供关于JavaBean的方法,属性,事件以及其他特征的明确信息。 其主要方法如下:
getPropertyDescriptors():获得所有属性描述器。 getBeanDescriptor():获得对象描述器。 getMethodDescriptors():获得所有方法描述器。 getEventSetDescriptors():获得所有事件描述器。 public class Demo public static void main (String[] args) throws IntrospectionException BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Person.class, Object.class); BeanDescriptor beanDescriptor = beanInfo.getBeanDescriptor(); PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); MethodDescriptor[] methodDescriptors = beanInfo.getMethodDescriptors(); EventSetDescriptor[] eventSetDescriptors = beanInfo.getEventSetDescriptors(); } }
BeanDescriptor java.beans.BeanDescriptor,即对象描述器。它提供了一个JavaBean的全局信息,例如JavaBean的类型,类名等信息。
我们一般是从BeanInfo对象获取BeanDescriptor对象,不过也可以直接通过new BeanDescriptor(Class beanClass)构造函数获取。
public class Demo public static void main (String[] args) throws IntrospectionException BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Person.class, Object.class); BeanDescriptor beanDescriptor = beanInfo.getBeanDescriptor(); Class<?> beanClass = beanDescriptor.getBeanClass(); Class<?> customizerClass = beanDescriptor.getCustomizerClass(); String displayName = beanDescriptor.getDisplayName(); String name = beanDescriptor.getName(); System.out.println("beanClass:" + beanClass); System.out.println("customizerClass:" + customizerClass); System.out.println("displayName:" + displayName); System.out.println("name:" + name); PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); MethodDescriptor[] methodDescriptors = beanInfo.getMethodDescriptors(); EventSetDescriptor[] eventSetDescriptors = beanInfo.getEventSetDescriptors(); } }
输出结果如下:
beanClass:class com.nobody.Person customizerClass:null displayName:Person name:Person
PropertyDescriptor java.beans.PropertyDescriptor,即属性描述器。描述了Java Bean的一个属性,通过一对读取方法。即PropertyDescriptor里面封装了JavaBean的其中一个属性的相关信息(例如属性名,属性类型,get和set等方法)。其主要方法如下:
getName():获得属性名。 getPropertyType():获得属性类型。 getReadMethod():获得用于读取属性值的方法。 getWriteMethod():获得用于写入属性值的方法。 setReadMethod(Method readMethod):设置用于读取属性值的方法。 setWriteMethod(Method writeMethod):设置用于写入属性值的方法。 public class Demo public static void main (String[] args) throws IntrospectionException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException { BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Person.class, Object.class); Person person = new Person(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), "Mr_nobody" , 18 ); PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) { Class<?> propertyType = propertyDescriptor.getPropertyType(); String propertyName = propertyDescriptor.getName(); Method readMethod = propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod(); Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod(); System.out.println("属性名:" + propertyName); System.out.println("属性类型:" + propertyType); System.out.println("写方法名:" + writeMethod.getName()); System.out.println("读方法名:" + readMethod.getName()); if ("age" .equals(propertyName)) { writeMethod.invoke(person, 20 ); } System.out.println("属性值:" + readMethod.invoke(person)); System.out.println("------------------------------------------" ); } } }
输出结果:
属性名:age 属性类型:int 写方法名:setAge 读方法名:getAge 属性值:20 ------------------------------------------ 属性名:id 属性类型:class java.lang.String 写方法名:setId 读方法名:getId 属性值:a6ccda55-c895-438e-893f-7fa448aba35a ------------------------------------------ 属性名:name 属性类型:class java.lang.String 写方法名:setName 读方法名:getName 属性值:Mr_nobody ------------------------------------------
当然,除了从BeanInfo对象获取PropertyDescriptor对象,也可以直接new的方式获取。
PropertyDescriptor namePropertyDescriptor = new PropertyDescriptor("name" , Person.class);
MethodDescriptor java.beans.MethodDescriptor,即方法描述器,通过它可以获取到类相关的方法,如下所示:
public class Demo public static void main (String[] args) throws IntrospectionException BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Person.class, Object.class); MethodDescriptor[] methodDescriptors = beanInfo.getMethodDescriptors(); for (MethodDescriptor methodDescriptor : methodDescriptors) { Method method = methodDescriptor.getMethod(); System.out.println(method); System.out.println("方法名:" + method.getName()); Type[] genericParameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes(); if (genericParameterTypes != null ) { for (Type genericParameterType : genericParameterTypes) { System.out.println("方法参数类型:" + genericParameterType.getTypeName()); } } Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType(); System.out.println("方法返回类型:" + returnType.getTypeName()); System.out.println("---------------------------" ); } } }
输出结果如下:
public java.lang.String com.nobody.Person.getName() 方法名:getName 方法返回类型:java.lang.String --------------------------- public void com.nobody.Person.setId(java.lang.String) 方法名:setId 方法参数类型:java.lang.String 方法返回类型:void --------------------------- public void com.nobody.Person.setAge(int) 方法名:setAge 方法参数类型:int 方法返回类型:void --------------------------- public void com.nobody.Person.setName(java.lang.String) 方法名:setName 方法参数类型:java.lang.String 方法返回类型:void --------------------------- public int com.nobody.Person.getAge() 方法名:getAge 方法返回类型:int --------------------------- public java.lang.String com.nobody.Person.getId() 方法名:getId 方法返回类型:java.lang.String --------------------------- public java.lang.String com.nobody.Person.toString() 方法名:toString 方法返回类型:java.lang.String ---------------------------
内省应用 在项目实战中,我们一般使用最多的是 Introspector,BeanInfo,PropertyDescriptor,这三者结合起来使用。
比如,我们通过内省可以实现,JavaBean和Map互转,不同JavaBean对象属性拷贝等功能。
public class BeanUtils public static <T> Map<String, Object> beanToMap (T bean, boolean putIfNull) throws IntrospectionException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException { if (bean == null ) { return new HashMap<>(); } Map<String, Object> returnMap = new HashMap<>(); BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(bean.getClass(), Object.class); PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) { String propertyName = propertyDescriptor.getName(); Method readMethod = propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod(); Object value = readMethod.invoke(bean); if (value == null && !putIfNull) { continue ; } returnMap.put(propertyName, value); } return returnMap; } public static <T> List<Map<String, Object>> beansToMaps(List<T> beans, boolean putIfNull) throws IllegalAccessException, IntrospectionException, InvocationTargetException { if (null == beans || beans.size() == 0 ) { return new ArrayList<>(); } List<Map<String, Object>> result = new ArrayList<>(beans.size() + 1 ); for (Object bean : beans) { result.add(beanToMap(bean, putIfNull)); } return result; } public static <T> T mapToBean (Map<String, Object> map, Class<T> clz) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, IntrospectionException, InvocationTargetException { T bean = clz.newInstance(); if (null == map) { return bean; } BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(clz, Object.class); PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) { String propertyName = propertyDescriptor.getName(); Object value = map.get(propertyName); Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod(); writeMethod.invoke(bean, value); } return bean; } public static <T> List<T> mapsToBeans (List<Map<String, Object>> maps, Class<T> clz) throws InvocationTargetException, IntrospectionException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException { if (null == maps || maps.size() == 0 ) { return new ArrayList<>(); } List<T> result = new ArrayList<>(); for (Map<String, Object> map : maps) { result.add(mapToBean(map, clz)); } return result; } public static <T1, T2> void copyProperties (T1 origin, T2 dest, boolean setNull, String[] excludeFieldNames) throws IntrospectionException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException { BeanInfo originBeanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(origin.getClass(), Object.class); PropertyDescriptor[] originPropertyDescriptors = originBeanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); BeanInfo destBeanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(dest.getClass(), Object.class); PropertyDescriptor[] destPropertyDescriptors = destBeanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : destPropertyDescriptors) { String propertyName = propertyDescriptor.getName(); boolean excludeField = false ; if (excludeFieldNames != null ) { for (String excludeFieldName : excludeFieldNames) { if (Objects.equals(excludeFieldName, propertyName)) { excludeField = true ; break ; } } } if (excludeField) { continue ; } for (PropertyDescriptor originPropertyDescriptor : originPropertyDescriptors) { String originPropertyName = originPropertyDescriptor.getName(); if (Objects.equals(propertyName, originPropertyName)) { Method readMethod = originPropertyDescriptor.getReadMethod(); Object srcValue = readMethod.invoke(origin); if (srcValue != null || setNull) { Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod(); writeMethod.invoke(dest, srcValue); } break ; } } } } public static <T1, T2> void copyProperties (T1 origin, T2 dest) throws IllegalAccessException, IntrospectionException, InvocationTargetException { copyProperties(origin, dest, false , null ); } }
以上是我们手写的JavaBean相关的转换工具类,当然市场上已经有很多成熟的工具包了,例如Apache的commons-beanutils包,里面就提供了许多实际开发中的应用场景会用到的API,大家不妨可以试用看看。
注意事项: getReadMethod()获取不到方法,所以出现空指针。
反射与内省的区别 内省操作只针对JavaBean,只有符合JavaBean规则的类的成员才可以采用内省API进行操作,而反射则不同,一个类的所有成员都可以进行反射操作。 内省和反射的操作也有很大不同,内省是先得到属性描述器PropertyDecriptor后再进行各种操作,反射则是先得到类的字节码Class后再进行各种操作的。 Java的内省最终是用Java的反射实现的。那为什么不直接用反射,要使用内省呢?
使用内省替代直接使用反射可以防止破坏类的封装 我们定义一个人的类型,其中包括年龄和是否成年两个属性。在修改年龄属性的时候会同时修改是否成年的属性。我们假设18岁和18岁以上就是成年,否则就是未成年。
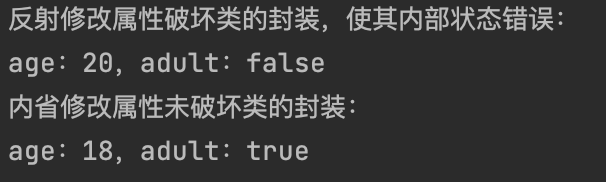
import java.beans.IntrospectionException;import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.text.MessageFormat;class Person private static final int ADULT_AGE = 18 ; private int age; private boolean adult; public int getAge () return age; } public void setAge (int age) this .age = age; this .adult = age >= ADULT_AGE; } public boolean isAdult () return adult; } public String toString () return MessageFormat.format("age:{0},adult:{1}" , age, adult); } } public class Test public static void changeObjectFieldByReflection (Object o, String fieldName, Object value) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException Field field = o.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(o, value); } public static void changeObjectFieldByIntrospector (Object o, String fieldName, Object value) throws IntrospectionException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException PropertyDescriptor pd = new PropertyDescriptor(fieldName, o.getClass()); pd.getWriteMethod().invoke(o, value); } public static void main (String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IntrospectionException, InvocationTargetException Person p = new Person(); changeObjectFieldByReflection(p, "age" , 20 ); System.out.println("反射修改属性破坏类的封装,使其内部状态错误:" ); System.out.println(p); changeObjectFieldByIntrospector(p, "age" , 18 ); System.out.println("内省修改属性未破坏类的封装:" ); System.out.println(p); } }
可以看到,反射由于是直接修改属性,所以破坏了类中封装的逻辑(20岁却不是成年)。
而内省由于修改属性还是调用了set方法,也就是说和正常修改对象属性调用了相同的方法,所以类的封装性不会遭到破坏。
当然由于内省其实本质也是反射,可以说是封装了反射,所以如果反射用的正确,也是安全的,我们可以根据属性名去获取相应的set和get方法,然后再去调用,但是这种情况下内省使用起来就更方便,毕竟没有必要重复发明一个车轮子,圆形轮子已经是很多年很多年智慧的结晶了。
那么问题来了,既然内省就是调用set和get方法,那我为什么不直接调用set和get方法,而要使用内省呢?
使用内省也一样可以写出通用的工具 既然内省可以动态获取信息,那就和反射一样,可以实现出通用工具或者框架哦。我们这里实现一个可以拷贝任意类型两个对象的属性值的工具方法。
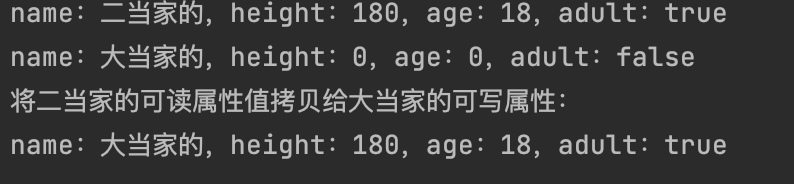
import java.beans.BeanInfo;import java.beans.IntrospectionException;import java.beans.Introspector;import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.text.MessageFormat;class Person private static final int ADULT_AGE = 18 ; private final String name; private int height; private int age; private boolean adult; public Person (String name) this .name = name; } public String getName () return name; } public int getHeight () return height; } public void setHeight (int height) this .height = height; } public int getAge () return age; } public void setAge (int age) this .age = age; this .adult = age >= ADULT_AGE; } public boolean isAdult () return adult; } public String toString () return MessageFormat.format("name:{0},height:{1},age:{2},adult:{3}" , name, height, age, adult); } } public class Test public static <T> void copyProperties (T dest, T orig) throws IntrospectionException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(orig.getClass()); PropertyDescriptor[] pds = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); for (PropertyDescriptor pd : pds) { Method rm = pd.getReadMethod(); Method wm = pd.getWriteMethod(); if (rm != null && wm != null ) { Object value = rm.invoke(orig); wm.invoke(dest, value); } } } public static void main (String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IntrospectionException, InvocationTargetException Person p2 = new Person("二当家的" ); p2.setAge(18 ); p2.setHeight(180 ); System.out.println(p2); Person p1 = new Person("大当家的" ); System.out.println(p1); System.out.println("将二当家的可读属性值拷贝给大当家的可写属性:" ); copyProperties(p1, p2); System.out.println(p1); } }
可以看到,名字没有被拷贝,其他的属性值都顺利拷贝了。这也是我们期望的结果。
内省很好的保证了类的封装性,同时又具有动态获取对象属性,和动态修改对象属性的能力。
总结 在标准的JavaBean中,可以考虑使用Introspector体系解析JavaBean,主要是方便使用反射之前的时候快速获取到JavaBean的Setter和Getter方法。 在Spring体系中,为了防止JDK对内省信息的缓存无法被垃圾回收机制回收导致内存溢出,主要的操作除了可以通过配置IntrospectorCleanupListener预防,还有另外一种方式,就是通过CachedIntrospectionResults类自行管理Introspector中的缓存(这种方式才是优雅的方式,这样可以避免刷新整个Introspector的缓存缓冲区而导致其他应用的Introspector也被清空),也就是把Jdk自行管理的Introspector相关缓存交给Spring自己去管理 。在SpringBoot刷新上下文的方法AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()中finally代码块中存在清理缓存的方法AbstractApplicationContext#resetCommonCaches();,里面调用到的CachedIntrospectionResults#clearClassLoader(getClassLoader())方法就是清理指定的ClassLoader下的所有Introspector中的缓存的引用。 参考文章:聊聊Java内省Introspector (qq.com) 大多数人不知道的Java知识 - Java内省机制 - 知乎 (zhihu.com) Java的反射(Reflection)和内省(IntroSpector)机制 - SegmentFault 思否 java的反射用不好容易走火入魔?还可以用内省啊!-阿里云开发者社区 (aliyun.com)